You may not be a candidate for resective surgery because:
- The area where the seizures start cannot be clearly identified or localized with the tests performed.
- A previous surgery did not work as expected.
- The area where the seizures start is responsible for very important brain functions like memory, speech, etc.
- It is contraindicated due to other medical conditions.
Other treatment options are available for people with drug-resistant epilepsy who meet the criteria mentioned above.
With the advances in technology, medical devices have been developed and approved as safe and effective alternatives for those who are not candidates for resective surgeries.
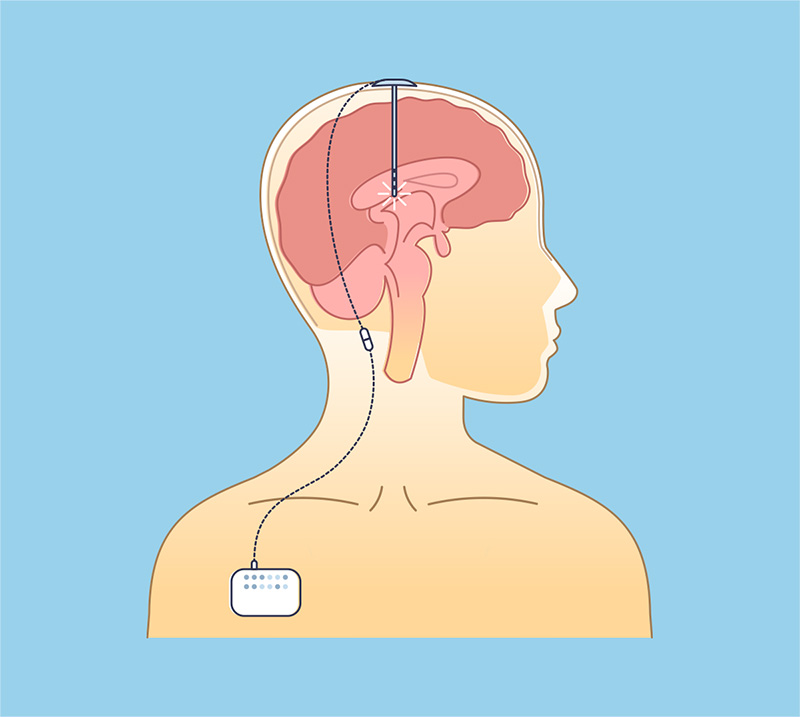
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a procedure in which electrodes (leads) are implanted deep into the brain to stimulate different areas to control seizures. DBS has been considered another safe and effective procedure and has been used for the treatment of multiple diseases in the nervous system like Parkinson’s disease.
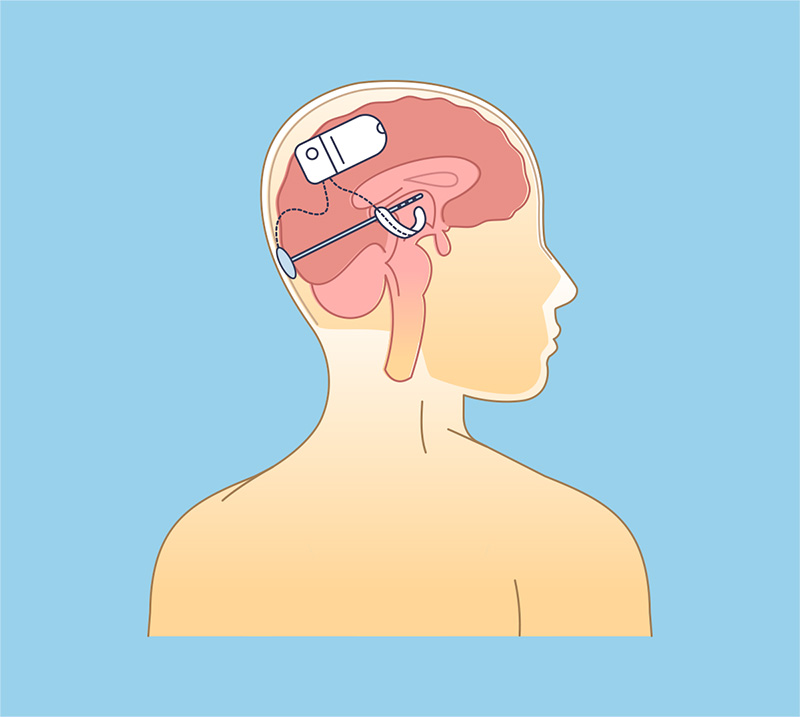
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS)
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS), also known as brain-responsive neurostimulation consists of a system that includes a programmable generator (stimulator), flexible wires (leads) and an external device called programmer. The goal of RNS is to reduce the frequency and severity of the seizures by sending electrical stimulation to reduce abnormal activity in the brain.
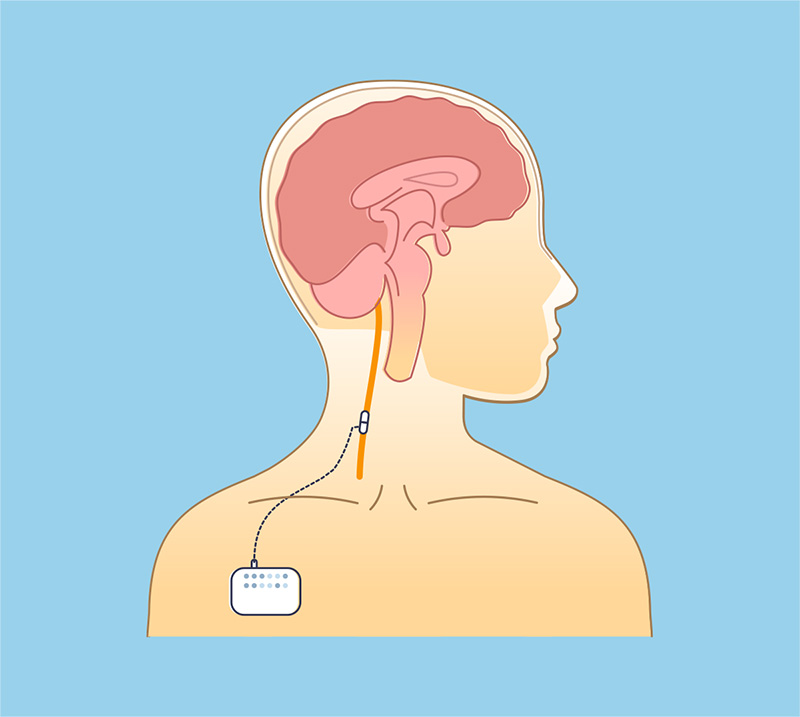
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) works with a small generator that sends electrical signals to the brain through the vagus nerve disrupting abnormal brain activity that causes seizures. The goal of VNS is to reduce the number and severity of the seizures.
Ask your doctors if you might be a candidate for any of the neurostimulation surgeries and learn about the potential benefits and risks for you.



